Rectilinear Propagation of light
- a
new concept and understanding
Salient Points
1) The reason, phenomenon and the analysis on rectilinear propagation
of light is elaborated in Part I and our critical views in Part II. Both represent the same matter.
2) 'The Deviation' - reason and phenomenon, is copy right matter (No-
16600/97) with the copyright office Govt. of India. ( for full text ....click here)
3) The deviation is the bending property of light rays when passing
from rarer to denser or denser to rarer medium.
4) Rectilinear propagation of light is generally accepted concept
before the 'wave theory of light' was put forward.
5) To explain and establish the concept of rectilinear propogation
of light, Newton had put forward his corpuscular theory of light and had explained reflection and refraction on the basis
of that theory. But after Newton, his followers could not explain the later phenomenon of wave theory viz interference, diffraction
and polarization. Hence wave theory was accepted as wave nature of light.
6) The reflection and refraction of light is explained on the basis
of wave theory, though the geometrical optics is totally based upon rectilinear propagation of light, and no body had denied
or rejected this, either in whole or in part.
7) The bending of ray of light is due to change in the medium, as
when light passes through prism and lens, dispersion is a molecular phenomenon, due to molecular gradiant of material of the
prism or lens or the medium through which it passes. The reason for deviation in elementary books on physics clearly show
that, ( as illustrated in item 1 and 2 of 'The Deviation') if the angle of prism reduced to zero the bending reduces to zero
i.e there is no bending. Which is also the case, if the refractive index becomes identical to out side ambient conditions.
This shows that, within the same medium bending is not there.
8) Therefore, I state that unless there is a change in the medium,
change in the path of light is not possible or vice versa.
9) Hence wave nature explained
on the basis of wave theory, for propogation of light, is not so in reality and wave length or wave nature in light rays is
non existent.
10) Further the wave motion is supposed to be in space due to some
highly elastic and rare ether particles. The properties stated of this hypothetical medium denote that of existing matter.
There is hence this contradiction that hypothetical medium cannot have properties of existing matter or existing matter cannot
remain hypothetical.
Thus wave theory of light is based upon improper hypothesis and also
wave motion cannot take place under high velocities of light rays.
11) Thus wave motion is not the character of light rays, and wave
length does not exist and is not the reality.
12) Interestingly, I have ascertained that, when bending takes place
adjoining a physical obstacle or sharp edge, then there is some medium existing associated with the solid state of matter,
and having very high attraction towards the center of mass. In the case of liquids and gases, which are loose particle state
of matter, the medium is not perceivable at the surface.
This medium is not a liquid. It is not gas but gas like, having its
own refractive index and state.
13) For example Fig X, explains, the existence of this medium and
patterning in the slit, by virtue of the properties and character of this medium. In this case, the pattern in the slit takes
the shape of double cylindrical diverging lens of long focal length, giving rise to a patterned image on the screen. Till
now commonly we call this as 'fringes' and we say they are maximum energy portions from wave front which adds to brightness
on screen or minimum energy portions, which adds to darkness [of course using coherent sources to see clear pattern). But
it is my conjecture that the character of patterns at the slits generated by this associated medium adds to brightness or
darkness, and not the energy portions. Therefore statement of Thomas Young saying that the light adding to light under certain
conditions produces darkness, is not true and fringes on the interference screen are not fringes but proper orders of spectrum
arising from each section of diverging lens of long focal length from this unique medium. This is the reason that there is
no light beyond say 10 degrees to 90 degrees on either side of the slit.
14) The existence of the medium is not visible usually as refractive
index is below that of water, hence it is not visible under optical instruments, while a slit made up of two razor blades,
produces pattern on adjusting this slit, and we can see the pattern with naked eyes, in open day light, and not in front of
direct light source. If this slit is filled half with water it can be seen that the fringes existing are not disturbed by
water, in the slit. It means medium is intact in water and does not exist over surface of liquid as with solid state of matter.
It also shows that Newton’s rings are not due to interfering waves, but due to the character of medium and fringes by
virtue of the medium as stated in properties. In Newton’s rings wedge is that of medium trapped with in the two solid
surfaces, one glass plate and other lens giving shape of circular wedge of medium [magic of slit page 8]
15) Diffraction is similar for the source near the slit [Fresnel ‘s
diffraction] and source at infinity [franhoper’s diffraction ] and is again due to multiple slits but in terms of fine
spectrum
16) Polarisation - The existent
medium at the plain surface [as per properties page 5]such as in plain sheets, gives rise to patterns at certain angle, which
combine with each other and if the reflector is rotated, the pattern goes away at right angle [as in plain polarimeter], but
not due to the nature of waves i.e. Vibrations cut one side and remain on other side
17) 'Part II' relates to criticism and outcome of some simple experiments
in elementary physics, this can be sent, if asked individually.
If you wish to send your comments or
receive more information on this article, please record
details hereunder:

My Guestbook Our contact details: Please email at: ocsharma1@hotmail.com

Analysis and critical views
O.C.Sharma
The Concept of Rectilenier Propogation of Light
Table of Contents
PART
1
GENERAL
IDEA 1
RECTILINEAR PROPOGATION OF LIGHT 2
Deviation 3
Properties of the field or fluid 5
The Magic of the Slit
7
Interference and Diffraction of Light 8
Polarization 9
PART
2
CRITICISM
AND OUTCOME OF SIMPLE EXPERIMENTS 10
Wave theory
and Nature of Light 10
Periodicity
10
Wave Formation 10
Sea Waves 11
Surface Tension 11
Capillarity, rise of water in plants and anti-gravitational
growth 12
Michelson and Morley's experiment 13
Inactiveness of the Medium 13
Part 1
General
Idea
The “deviation” is bending property of light passing from one transparent medium to other transparent
medium. It is well explained in geometrical optics, but it is also that light bends round the obstacles, corners and sharp
edges, where no other medium is expected and this bending was difficult to explain on the bases of geometrical optics, which
was explained on the basis of new theory called wave theory, which explained the reflection, refraction and polarisation which
can’t be explained on the basis of classical geometrical optics hence wave theory was accepted as reason of such bending
of light and motion was said to be wave like and not the rectilinear.
But I say that unless there is change in the medium there can’t be any change in the path
of light and if the path of light changes there must be some reason or medium. This reason and medium is explained in this
paper i.e. the deviation and wave theory is not the reason or wave like motion for propogation of light which is again based
on hypothetical medium called ether which is partly given the properties of matter and partly hypothetical , which is not
possible with the matter existing. Elasticity is the property of matter existing, if the ether posses this property then it
must exist , but all efforts to detect it had failed and if hypothetical , how it can carry such high speed motion . Therefore
answer to this question is in this paper the Deviation. The matter is in two parts. Part one is as under:
THE CONCEPT OF RECTILINEAR PROPOGATION OF LIGHT
It is known for a long time
that light travels in a straight line. Probably , this was believed due to light falling over an object and casting an image
or shadow exactly opposite to the source of light. A simple experiment performed in the laboratory i.e. two pin holes are
in one and exactly in straight line, revealed that light travels in a straight line.
An attempt made by Mr. Fermat
to show that if light follows longer path but proved that light never chooses longer path but always the shortest one to travel.
There were however proofs but based on simple and common observations. A scientific approach in the subject was the requirement
to have some valid and concrete results but this was not possible in one and the same medium. Therefore passing of light from
one medium to the other medium was the matter of interest and giving some results. The straight line path of light was found
bending in the other medium with respect to one from which it enters the second medium. Therefore to study the behavior of
light the change in the medium was required, but it was not possible to take as whole medium, therefore short form of medium
was required for the laboratory purposes, hence rectangular slabs, prisms and lens were taken for the laboratory purpose as
other medium water or air do not have any shape hence can be taken into other suitable vessels. The bending of light in different
media revealed some consistency in bending which resulted into a common factor for each material as degree of transparency
or commonly known as refractive index of that material or for that type of material. Even though if one instrument is taken
say glass slab , we can't proceed to any result unless we are having its definite geometrical and calculatable dimensions.
Therefore
the glass slab , lens or prism taken as other medium but having definite geometrical shape. The passing of the light from
them is always bending depending upon the geometry and shape of the instrument and also the degree of transparency of the
material , it is the object of the matter that why bending takes place and if bending takes place then is there any reason
for that?
Later it was observed by some of the Research workers that when light passing round the obstacles, sharp
edges and corners it bends and there was no medium other than normal air then how light was found bending , to answer this
question a new theory of light came forward with explanation that why light bends near the corners and edges. This bending
of light was explained on the basis of wave theory, proposed by Christian Huygens and supported later by some eminent Scientists
the bending was found or stated purely as light behavior, therefore no question of other medium to deviate the ray of light
, therefore no consideration of geometry of the medium, and the nature of propagation was termed as wave nature.
Though
this theory could explain most of the phenomenon including reflection , refraction but the previous theory based on geometrical
aspects could not explain this sort of bending in absence of the other medium. Therefore the new theory proposed by Christian
Huygens was accepted as the reason for this sort of bending , or accepted as wave theory. Further the phenomenon of interference
, diffraction and polarization explained on the basis of this theory could not be explained on the basis of Geometrical optics,
in this theory i.e. wave theory , light is believed to travel in the form of waves and not in a straight line.
Though
the rectilinear propogation of light was tried to explain by Issaq Newton and he had put forward a theory known as corpuscular
theory and tried to explain the reflection and refraction on the basis of this theory but later people failed to explain the
latter phenomenon viz. Interference , diffraction and polarization. Therefore wave theory accepted as the reason of bending
and wave like motion of light and not as straight line motion.
Though wave theory explained that light propogates in
space in the form of waves and due to this nature or wave motion, we get dark and bright bands of light on interference screen
, which the theory states that it is due to interaction and addition of the maximum energy portions of two waves or addition
and interaction of two minimum energy portions of two waves. Similarly there is darkness behind the slit giving interference
or diffraction pattern. Perhaps based upon this is pointed out by Mr. Thomas Young that light adding to light under certain
circumstances produces darkness. Later darkness behind the slit is tried to explain by Mr. Frasnel mathematically using Carnu's
spirals. It is merely mathematical approach. Further bending round the corners or edges , I mean to say that this is not due
to wave nature and statement of Thomas Young and Carnu's spirals explained , the darkness behind the slit is not the answer
or clear. Therefore deviation is an attempt to find the reason for bending , and to explain how light adding to light under
certain circumstances produces darkness or adds to intensity , also reason for darkness behind the slit. The matter will be
taken in to two parts , the 1st part will consist of reasoning and phenomenon , the 2nd part will consist the criticism and
some outcome of some simple phenomenon existing in nature and including some already known simple experiments in elementary
physics.
THE DEVIATION
I shall take the three instruments viz. the rectangular glass slab , lens and the
prism as change in the medium. As the reflection is the same medium phenomena therefore only refraction will be taken into
consideration for the purpose. Further if we go through the geometrical shape of the instruments, we find that the rectangular
slab is bounded by six parallel surfaces. If a ray of light incident normal to any surface that undergoes no change in the
path , whether rare to denser medium or denser to rare medium , but when a ray incident at an angle with the normal that bends
in the denser medium towards the normal and when emerging out it goes away from the normal but parallel to incident ray also
having a certain shift from the incident ray.
If we see the prism , it is bound by five surfaces , it is as if the
top surface of rectangular block is missing and the two side surfaces meeting at top and making the angle of prism. Any ray
passing from rare to denser medium in this prism at an suitable angle with normal it undergoes double i.e. ray splits up into
constituent colours i.e. in prism a ray undergoes double bending and dispersion simultaneously.
A
A B
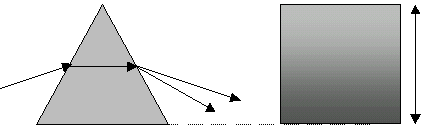
B a C
C b D
molecular gradient normal to the bottom B C
(a) Dispersion due to ordinary prism
(b) Same prism (a) just open at apex A
with the same content of matter in (b) as of (a) that is same no. of molecule
The same spectrum and dispersion is possible due to molecular gradient normal to
the path of light.
If we see some such other
instruments i.e. an instrument bounded by four surfaces is not useful for the purpose and one, bounded by three surfaces do
not exist and another bounded by two surfaces but having zero width is useless and one plane is merely an area. But an instrument
bounded by two curved surfaces is very useful, it can be cut section of a sphere or common section of two spheres of equal
or unequal diameters. When a ray of light falls at the center of lens normally it passes along the axis and do not bend again
if ray falls over at any point of curved surface of lens normally or at an angle emerges out as dispersed and passes through
the focus, different colours through different focii.
It is clear from above
that through there is a change in the medium but bending is not always there but under one condition or other bending is there with the change in the medium whenever there is bending that is due to one factor that the
degree of transparency or commonly known as refractive index of that material of the medium. Further if we go through the
relation for deviation produced by prism that is d = A(n-1) where d = deviation produced
, A= angle of prism and n = refractive index of the material of the prism , we see that if we reduce the angle of the prism
to zero we find that prism reduces the expression into zero. If we put n – 1 = 0 or n = 1 we see that product again
reduces to zero which means there will be no deviation if the refractive index outside the prism is same or transparency inside
prism becomes similar to outside prism i.e. similar or the same medium , means with in the same medium no deviation , which
means any change in the path of light is not possible unless there is a change in the medium or unless there is any change
in the medium , change in the path of light is not possible.
Hence light is bound by
virtue of itself to travel in straight line. It is also clear that within the same medium light will travel in straight line.
And now we shall see why dispersion takes place?
Dispersion is broadly
possible in prism as the simplest case and let us consider the passing of light through prism as prism is bounded by five
surfaces. The two side surfaces look to be meeting at apex as if top surface is missing and if these three surfaces will be
equal , then they will be having equal and opposite angles and the prism can be in the shape of equilateral triangle , if
one side is small the opposite angle will be small And prism will
be called small angle prism. Anyhow this angle has very important role for dispersion. It means two normals drawn on the two
surfaces are never parallel. Hence any incident ray one surface will undergo double bending in prism and because of angle
of prism dispersion will take place, but why dispersion , let us see the prism as a parallelepiped or let prism be open from
apex in such a way that prism becomes a parallelepiped and the concentration of the molecules of the materials of prism varies
at top but remains same at bottom which forms the molecular gradient from bottom to top and the mass and volume of the prism
remains same or more precisely it will be the concentration gradient of the molecules which rarified at top due to the opening
of two sides and normal to the bottom. When a ray of light passes through such a slab there will be dispersion because of
concentration of gradient of molecules normal to the path of light, means the ray of light faces less numbers of molecules
one side and more number of molecules on the other side normal to the passage of light.
It is actually not possible
to have such an arrangement practically in practice or in solid state of matter but can be achieved in liquid if we put some soluble salt or sugar in water and without stirring or disturbing liquid we have this sort of
condition but not useful. It is only to understand the reason.
But it occurs in nature
itself it is nothing but our gaseous atmosphere over the earth as gases are matter hence possesses weight and are attracted
towards the center of the earth. The heavier being denser with the surface of the earth
and the lighter ones rarified with the height or in other words the concentration goes on decreasing with the height and rarified
to vacuum several miles above.
This may have any usefulness
to the human beings or not, but this concentration gradient occurring in nature is responsible for dispersion of light and
we daily see redness of the sky at the rising and setting of the sun. Redness is always visible
having low angle of deviations
whereas violet not visible as it mixes up with dark at that time.
We got dispersion with
prism because of concentration gradient by virtue of angle of prism which makes the condition with the same homogeneous medium
in the prism as when a ray of light passes through prism it passes through molecular concentration gradient along the path
of light more number of molecules on one side and less number of molecules on the other side. Hence it or dispersion is a molecular phenomena provided the light can pass through
medium or medium is transparent to light. This dispersion is also produced by lens, as lens also acts as a small angle prism
therefore producing very small angle of dispersion hence when white light is passed through lens, image is tinged with end
colours which is called colour defect of the image or lens, which is actually dispersion due to small angle of the prism i.e.
of a lens and not the defect.
Now let us see the bending
of the light around corners and edges. It is the basic conclusion of the physical optics that light bends around corner and
edges, without any reason but having wave like nature or propagation of light which is proved to be the reason of bending.
if there is no reason, in the light of previous discussion, we can say that if there is no reason, light ray should not bend,
wave like motion is property of matter or not , or it is really possessed by matter ? should it cause bending to a very high
speed traveling ray of light ? It is common observation that when a particle is moving at a very high speed its bending will
be very large. It cannot take turn at very very negligible space. Though bending will be due to some action of forces otherwise
not.
There are three states
of matter, and all are fairly known and studied large number of aspects related with the subject useful or not useful are
brought to light as science, information with wide applications useful to the human beings but can we imagine a unique field
of matter, that is not solid but under circumstances it may pass through some solid, it is not liquid but remains free , it
is not mixing with other matters like water or any other liquid or unaffected by liquid or gases. It is fluid like exists
free. It is some sort of field as existing in the form of unique field. If it is a material then it should have some common
properties with other states of matter but it has much less common properties, hence it is unique field.
In wave theory wave
nature or wave character is accepted as the reason of the light propagation in space. But this is not true. There is some
medium present at the edges or the corners which is responsible for bending of light though this is not known and being invisible
never recognized by any body. This is a unique field but not similar to any of the three states of matter those are already
known. Really it is not solid hence no shape , no weight but associated with the solid state of matter. It is not liquid hence
it does not flow and keeps its level horizontal besides this field keeps its character free in liquid hence totally different
from liquid. It is gas like but not gas and different from gas.
PROPERTIES
OF THE FIELD OR FLUID:
1) This fluid or field is
gas like but not gas , weight less but rigidly bound to the solid state of matter as it has an attraction towards the center
of the mass of the body irrespective of size and shape of the body
2) It exists in the form of layers over any surface
of solid state, for bigger bodies layers are thicker whereas with the small particles layers are fine. Further they reduce
a little in thickness i.e. grow thinner up to the boundary to which this field exists and within this boundary there are fixed
numbers of layers i.e. not unlimited. This shows that this fluid keeps its boundary itself.
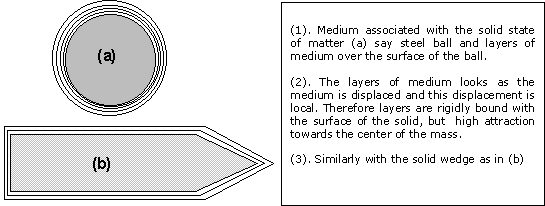
Further
if two bodies , say pencils or rods with spherical or parabolic ends or even hand fingers brought closer slowly the boundaries
over two ends ( or say at finger tips) cross each other distinctly as the field over the two ends do not affect each other
, but compresses a little and this or fine layer formation takes place there when two ends are brought little more closer
(straight edge).
DIAGRAM (a) below shows the medium exists over the surface of solid state of matter and
takes the shape of that surface. Let us have rod ends or even tips of our hands fingers and let them bring very close to each
other, so that the medium over ends cross each other portion 'A' 'B' as shown in the figure (a), portion 'A' 'B' is little
darkened. There are three such portions corresponding to three layers of medium, though with the open gap all the layers not
seen intersecting like 'A' 'B', which means that (1). Medium keeps its boundary itself and (2). The medium is discrete and
not continuous. The darkness in the gap spreads a little. When gap or ends brought little closer to each other and finally
medium becomes continuous over the surface when ends fully touch each other.

(a)
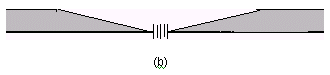
DIAGRAM
(b) above shows layer formation with a certain minimum width of slit made of two straight edges (closed gap) normal to the
plane of paper.
1) Existing of this field in the layer formation over a body is like a displaced medium by a body immersed in such a
medium and layer formation over the surface shows that medium is elastic but compression is local due to which layer formation
takes place at the surface of the body but not incompressible like liquid state of matter which is displaced as whole when
some solid or other volume is added to it.
2) It is not affected by water , therefore keeps its existence free and intact in water also. This means that it does
not exists like solid state with liquids.
3) It is transparent and refractive index is greater than air but below water hence less than any glass and not recognized under the optical instruments.
4) It is inactive towards the electricity or magnetism but can become active under
certain conditions e.g. if we say that when electricity is passed through discharge tube we say that the gases are non-conductive under normal
temperature and pressure hence electrical current does not pass in the discharge tube. But
when we go on decreasing pressure in discharge tube we see that current starts passing
due to ionization of gas molecules at low pressure but this is not the case. Actually gases are non-conductive to electric
discharge at any pressure but when gas in the discharge tube becomes rare and field becomes continuous then current starts
passing. Though character of glow can be that of residual gas but conduction of electricity is because of continuity of field.
The field is associated with the walls of the tube and is inactive in presence of pressure of gas but when gas goes out and
residual molecules remain in tube far apart, field becomes continuous and current starts passing.
8) It should be noted that it may be easy to remove a gas from a chamber but it is
difficult to remove this field . Henceforth I shall call this field or fluid as medium.
If this is the medium existing over the surface of the matter, then can it contribute to bending of light ? Or say how bending
takes place. When a ray of light passing through a corner or round the obstacle, it is clear from above that the medium existing
over surface, exists in the shape of that surface, of the body. For simple understanding
we can’t take an irregular body, but a smooth and regular body the medium existing over it will be in the shape of that
surface. For any sharp edge obviously medium will exist in the shape of that edge and that medium over such edge will appear
like a very small angle prism. Also from above , this medium over edge exists in the form of layers. The wide layer with surface
and gradually thin layers beyond or above but this is always fixed in number and exists up to the boundary of the medium,
which means that medium keeps its boundary itself.
Whenever a ray of light
incident normally to this edge , ray passes through this prism of the medium and due to very low angle of prism and low refractive
index ray deviates at a small angle. This prism of the medium over edge made up of layers looks like a prism composed of sections
of prisms of which the prism is made up of.
The bending of rays undergo
from each section and give rise to bands of black and white fringes with wider with edge and less wider up to the boundary
but this band or bands of fringes is not clear with the source near the edge or what we say the source emitting the spherical
wave front. This pattern is there but diffused with the overlapping of rays. Therefore for distinct and clear pattern we take
two such edges and place them opposite to each other to form a slit. With a certain minimum width of the slit this sort of
pattern is again obtained , but pattern is opposite to that of single edge i.e. if we go 2 (b) above i.e. if we take two pencils
or rods with spherical or parabolic ends and if we bring these two ends slowly close to each other we find that the medium
existing on both ends slowly cross each other whereas the boundaries of the medium over ends remain intact and cross each
other the common portion within the two boundaries becomes a little dark when seen
through bright atmosphere, but medium from both the sides compress a little i.e. to a certain minimum width within the tow
edges wide band or bright band go to the center and the less wider layers go to the wall sides of the edges. If these two
edges are brought more close to each other this pattern remains steady for a moment and collapses just before the edges touch
or meet together, but before touching the two edges medium becomes dark and spreads like the field is attracted by the walls
of the edges in the gap and the pattern vanishes.
This is the formation
of the slit in all interference and diffraction experiments, but when the source is near the slit the pattern is not clear
because of so called spherical wave front or overlapping rays. Therefore the pattern
is still diffused. Therefore in interference we have tried to get two similar or identical sources called coherent sources i.e. originated from the same source for the reason that to obtain same pattern of original.
Hence similar or coherent sources those have from same wave front, same path difference, same amplitude etc. but later we
will see that all this was not necessary but patterns form these coherent sources when cross each other at a suitable distance they add in intensity and become more clearly visible in the field of view of eye piece.
These two similar or coherent
sources produced with the image of one or primary in Lloyds’ mirror or the two
patterns produced by fresnel’s biprism. in both the cases the clear pattern or the character of pattern is carried by
light rays or made visible and deviate through very small angle prisms or similarly in Lloyds’mirror the patterns get
added at a certain distance and pattern becomes fairly visible in the field of view.
Now let us see that why
bending takes place. The existence of medium in layer formations over the surface and over an edge is similar, it is only
that the shape of the layers is like that of the surface exposed. In case of two edges
brought very close to each other the medium existing over one single edge is similar in layer formation but patterns are different
to those the two edges come to very close to each other. In case of two edges when come close we find that two prisms of very
small angle meet at their apexes. When such edges brought further close to each other the pattern remains steady for some
time then collapses before the meeting of the edges practically.
When we say edge or a
prism of medium over edge we see two things one the shape of the medium is like that of edge hence medium over edge behaves
as a small angle prism. Further layer formation renders this prism as this is made up of numbers of sections of prism placed
one above the other to constitute one such small angle prism. This happens because of layer formations similar to convex lens
to which we assume that it is made up of number of sections to constitute one lens but lens has curvilinear surface against
what we have with prism. Still we get small dispersion due to small angle and different foci for different colours where we
usually say that this is the colour defect of the lens but this is the proper dispersion of low angle prism i.e. of lens hence
not defects.
When two such low angle
prisms of the media meet like edges or at apexes within the slit they take the shape of a double cylindrical diverging lens
of long or very long focal length within layer pattern inside the slit with broad layer
or band definitely at center due to the property of diverging lens, hence broad center on screen and gradually thin layers
decreasing in thickness towards the wall of edge. Hence on either side on screen as many number of layers are in the slit
those many are the fringes on the screen.
It is not the maximum
or minimum energy of light waves to interfere due to wave motion but each and single order of spectrum arising due to layer
formation as the individual sections of the low angle prism. Therefore under no circumstances
light adding to light produces darkness, but are proper orders of spectra what we say white or bright and dark bands are proper
orders of spectra. The bright portion is the part of the spectrum from yellow to red and the dark portion is from green to
violet. These two of dark and bright bands corresponds to one and proper order of spectrum
and system of bright and dark fringes or bands means system of spectra arising from such each layer of medium in slit.
The
bending is small because of low angle prism and low refractive index of the medium. And
because of small angle of the prism and small angle of deviation, Beyond this pattern there is no light or hundred percent
darkness not explained on the basis of wave theory and not possible to explain but attempt was made by Mr.Fresnel mathematically
and taking into account Carnu’s spirals to explain the darkness behind the silt that can be explained only that a double
cylindrical diverging lens of very long focal length made of such medium explained above and constituent of number of layers
as individual sections of prism deviate the light coming from slit at a very small angle and when whole the pattern from the
slit is transmitted on the screen how can be there light behind the slit beyond about
10 to 90 . Therefore the idea of wave length of light is of no use or meaningless. It can be the proportional quantity of
two or three parameters but not the waver length hence wave nature is the way adopted to explain the phenomena but not the
reality.
THE MAGIC OF THE SLIT :
The medium associated
with any edge is not visible or we do not see it practically but with slit made up of two razor blades, we can see this pattern
clearly with naked eyes
only in daylight but not
in front of a bright source. For this purpose let us have two razor blades and two
glass plates as edges then place these two blades within these two glass plates and tie these two plates with rubber-bands
so that the system will be rendered as solid unit. Now adjust the two blades to form
a slit. Bring them close to each other slowly so as to get the clear pattern of so
called fringes and actually setting of layers and see that they are steady. Fringes
can be counted as fixed in number not more or less if pattern obtained by adjusting
the slit again. This pattern is fairly visible with naked eyes provided we take this
slit into day light not in front of a direct source of light wherein flash light we shall not see the pattern though pattern
will be always there which is not the property of light but character of the medium explained above. Now let us fill this
slit half with water. One can see the existence of pattern within the water and out side of water is undisturbed and intact
but clearly visible, which shows that though this medium exists over the surface of solid state but not affected by water
and keeps its existence free from liquid. It also shows that this medium is not associated with the liquid state as with solid
state whereas it has greater attraction towards the center of mass. Why it has not attraction towers the liquid state ? And
it keeps its existence free ? Answer to this can be only that liquid state is the state of loose molecules and this medium
has greater attraction or energy so it goes to the binding energy of the molecules rather then existing over the surface.
Then medium existing with other solid body does not matter if placed in water or liquid or medium, it keeps its existences
free.
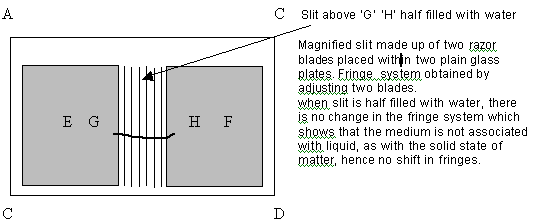
Similarly in case of free
molecules of gas this medium may be associated with the nucleus of the atom. As the gases are also a state of matter, hence
they also possess some other common properties of matter. Therefore the medium is rigidly bound to the solid state of the
matter and visible by some means. In the slit half filled
with water it also noted that there is hardly or no shift in the so called fringes outside water and inside water which means
the calculations of refractive index due to shift in fringes (which should be 1.5. times) is meaningless as attempted in Newton’s
rings. There can possibility that refractive index can be calculated with thick layers but not with extremely thin layers.
Further Newton’s rings are due to circular wedge or edge but only that of medium trapped within the glass plated and
lens. Hence reverse of solid edge but phenomena is same. Therefore calculations of wavelength are merely a calculation of
proportional quantity but not that of a wavelength.
Now I shall get to the
famous phenomenon of physical optics viz. The interference, diffraction and polarization of light. Actually these phenomenon came into the light because from Newton’s rings to
the development of the wave theory nobody recognized the existence of any sort of medium or such reason and assuming that
there is nothing at the corner, sharp edge or with the obstacle this sort or explanation was bound to come and that came after
the failure of rectilinear propagation of light i.e. concept to explain these phenomenon. Therefore if we have this sort of
medium explained above than the phenomena is self explaining.
INTERFERENCE AND DIFFRACTION OF LIGHT:
Interference is believed to be the interaction of waves i.e. similar waves in all respects, when these waves interact
with each other under suitable arrangement they produce black and white fringe system on the screen and believed due to wave
motion of light. Now if we get a Layer pattern in the slit without the direct source
but of course in daylight (merely to see where as pattern is character of medium not that of light and is always therewith
that width of slit of sharp edges only) then it is only the character of this pattern
carried out or made visible by light rays and when such two patterns with suitable arrangement like Lioyd’s mirror or Fresnel’s biprism, cross each other (rather than interacting)at suitable distance they actually
add in intensity and become fairly visible with the optical arrangement. Though this medium having low refractive index it
is not visible in most of the cases. Therefore no question of wave length or wave nature
at all. It is only miracle of the medium that takes the shape of a double cylindrical diverging lens in the slit and due to
layer formation produces such pattern which is carried by the light rays through the coherent sources and exposed on the screen,
when white light is passed through such slit these fringes or bands are tinged with colour as they are spectral orders originated
from small deviation of such lens and low refractive index of the medium. The deviation is small when source is near the slit,
when source is at infinity, only few rays pass through pattern and is much clear.
The difference in interference
and diffraction is first due to secondary sources in interference and direct obstacle in diffraction when source is near and
when source is at infinity it is other type of diffraction but grater deviation due to very fine system of layers with fine
grooves of said slits of grating. We also observe very wide single colour bands on the wire of a spider’s net at a suitable
angle of light.
The fineness and distinctness
of the fringes in Febry parrot Etalon is also due to the pattern trapped within the two semi
silvered plates and parallel light to give so called maximum and minimum energy of
light in the form of fringe system. In interference we say interaction of waves , we
get very fine and wide spectrum due to grating , where in diffraction grating we say the same in terms of spectral orders.
POLARISATION:
As
far as the polarisation is concerned we have considered the medium existing over an edge or sharp edge and medium takes the
shape of the edge or takes the shape of low angle prism but what happens if the medium exists over a plane surface , and a
ray of light incidents over such a plane surface. Definitely it takes the shape of
plane surface and the medium exists in the form of plane sheets over a plane surface. Similarly the layer formation exists
over surface up to boundary. If a ray of light passes along such surface the ray never passes straight but dip in the medium
at a very small angle and reflects in the same way over the surface . The ray will appear on the other side of the surface
diffused not distinct because of this medium present over the surface. If we decrease the angle with the normal or say the
case of plane polariscope (reflecting) the ray say incident at that angle of polarisation, the ray is said plane polarized
due to reflections. This polarised ray again incident and reflected by a plane and reflecting surface, in the same plane and
parallel to previous. This polarised ray will carry same intensity of light as polarized
ray reflected from 1st surface. When this 2nd surface is rotated through 90 degrees the light is cut
off or diminished. Actually what happens at this angle of polarization ray passing through such medium carry the character
of first pattern over second reflecting surface and when passing through second surface if this pattern is parallel to first
then patterns add each other and when rotated by 90 the pattern cross each other and do not add to intensity but if again
rotated by 9o i.e. total 180 then light again appear we say that light is plane polarized and light has Transverse vibrations
hence got cut at right angle to each other. It is nothing like Transverse vibrations. Those can pass through parallel slit
and stop through cross one but it only character or the pattern carried by the ray when parallel or ray passing through parallel
pattern at a certain angle , it adds to intensity and diminishes when cross to each other. Similar case when seen diffraction
round the obstacles we put a wire gauze in front of slit and see that the fringes with the wires parallel to slit appear in
the field of view and diminish those are cross to the slit. This does not mean that fringes are not with the wires those are
cross in the wire gauze if we rotate the wire gauze we see that condition remains the same, that whatever wires are parallel
to slit we get pattern of so called diffraction fringes. Therefore in plane polariscope with two reflecting surfaces. We do
not get any polarised light but patterns of or character of patterns of this medium over the two surfaces add to each other
when parallel and diminishes when cross each other. Similar case is with the polaroids.
For
double refraction it is also stated that light gets polarized and vibrations get separated in certain crystals, it happens
because crystals exist in layers and there exist certain boundaries between these layers that
split up light into two rays. This can be exhibited by and example of images seen in the window glasses at night when
there is dim light in room and dark outside. We see our face in even transparent glass plates when in a window we get two
such glasses at night very close to each other we see our two images of our face, it happens only due to a boundary between
two glass plates that is air and due to this boundary we get two images that actually within the glasses or in certain crystals
double refraction is due to a boundary between the two layers of crystal and not by cut of the vibrations to say light propogation
is of Transverse waves.
(1) © by Author
(2) Copies of this matter along with second part are available with the author, just for
postage only.
(3). Address : Mr.O.C.Sharma
Room
No. 2, Ram Dhari Chawl, Anand Gad Park Site Colony, Vikhroli, MUMBAI - 400 079, INDIA.

